HBV and Maternity
Hepatitis B Guidelines for Pregnant Women to protect their babies
What is hepatitis B?
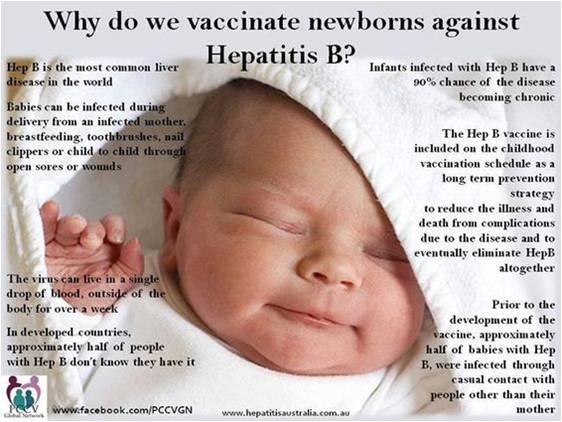
Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection in the world. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that attacks liver cells and can lead to cirrhosis (scarring) or cancer of the liver later in life. The virus is transmitted through contact with infected blood and bodily fluids.
If I am pregnant, should I be tested for hepatitis B?
Yes! Pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis B can transmit the virus to their newborns during pregnancy or delivery. Almost 90% of these babies will become chronically infected with hepatitis B at birth if there is no prevention. ALL
pregnant women should be tested for hepatitis B to prevent infection.
What if I test positive for hepatitis B while I am pregnant?
Although most women do not have any pregnancy complications as a result of HBV infection she should be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation. Although most women do not have any pregnancy complications as a result of HBV infection, it is still a good idea to be seen by a specialist.
How can I protect my newborn from hepatitis B?
If a pregnant woman tests positive for hepatitis B, her newborn child must be given the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine on Day 1, Day 30 and Day 60 with a booster at one year. If a baby does not receive these injections, then there is an up to 90% possibility that he or she will become chronically infected. However if on the rare occasions the vaccine does not work do not panic rigorous blood precautions by the mother can still protect the baby.
How do I protect my child if another family member is infected with hepatitis B?
Babies and children can be exposed to HBV from an infected dad, sibling, or other family member living in the same household. This can occur through contact with infected blood and bodily fluids. Vaccination is the best prevention against spreading the hepatitis B virus.
Can I breastfeed my baby if I am infected with hepatitis B?
Yes!
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) it is safe for an infected woman to breastfeed her child. All women with hepatitis B are encouraged to breastfeed their babies since the benefits of breastfeeding are huge in terms of building your babies immune system and since all newborns receive the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, the risk of transmission is zero.
How can I prevent getting hepatitis B if someone in my household is infected?
We recommend that anyone living in a household with an infected family member must be vaccinated AND tested for immunityi to HBV. This is especially important for babies and children since they are at greatest risk for developing a chronic infection if exposed to HBV at an early age. Until your 3 injection vaccine series is complete, it is important to avoid sharing any sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, or earrings, etc. since small amounts of blood can be exchanged through these items. Also, infected individuals should be careful to keep all cuts properly covered. Blood spills should be cleaned with gloves and a 10% bleach/water solution. Hepatitis B is not transmitted casually and it cannot be spread through sneezing, coughing, hugging, or eating food prepared by someone who is infected with Hepatitis B.
Remember that the best protection for you and your loved ones is the hepatitis B vaccine. Over 1 billion doses of the vaccine have been given, making it the most widely used vaccine in the world!